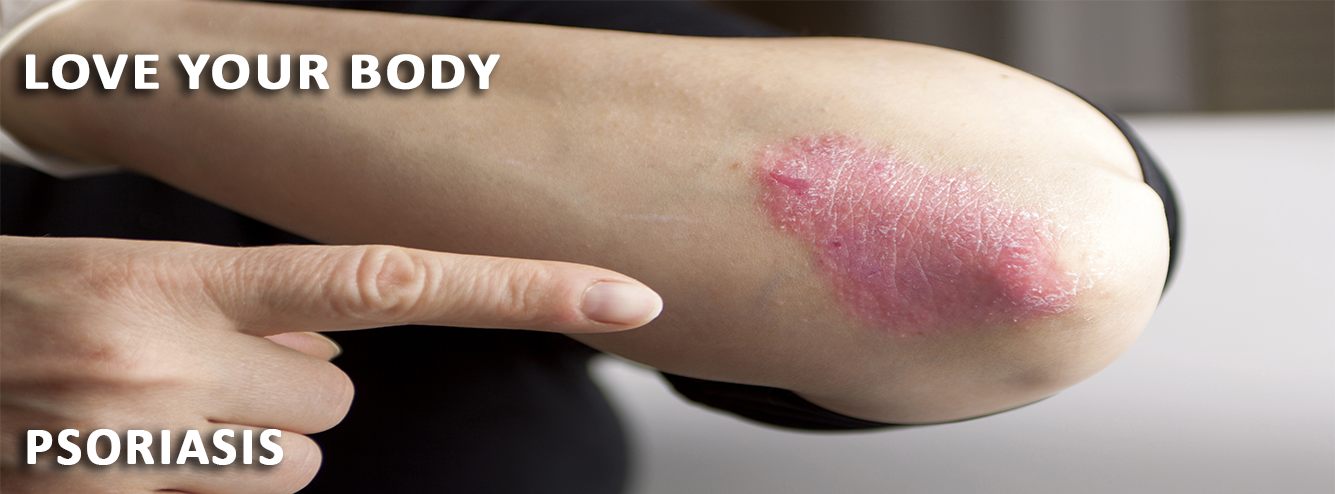

Psoriasis is a skin disorder that causes skin cells to multiply up to 10 times faster than normal. This makes the skin build up into bumpy red patches covered with white scales. They can grow anywhere, but most appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Psoriasis can't be passed from person to person. It does sometimes happen in members of the same family. Psoriasis usually appears in early adulthood. For most people, it affects just a few areas. In severe cases, psoriasis can cover large parts of the body. The patches can heal and then come back throughout a person's life.
The symptoms of psoriasis vary depending on the type you have. Some common symptoms for plaque psoriasis the most common variety of the condition include:
Plaques of red skin, often covered with silver-colored scales. These plaques may be itchy and painful, and they sometimes crack and bleed. In severe cases, the plaques will grow and merge, covering large areas.
Disorders of the fingernails and toenails, including discoloration and pitting of the nails. The nails may also crumble or detach from the nail bed.
Plaques of scales or crust on the scalp.
No one knows the exact cause of psoriasis, but experts believe that it is a combination of things. Something wrong with the immune system causes inflammation, triggering new skin cells to form too quickly. Normally, skin cells are replaced every 10 to 30 days. With psoriasis, new cells grow every 3 to 4 days. The buildup of old cells being replaced by new ones creates those silver scales.
Psoriasis tends to run in families, but it may be skip generations. For instance, a grandfather and his grandson may be affected, but not the child's mother.
Luckily, there are many treatments. Some slow the growth of new skin cells, and others relieve itching and dry skin. Your doctor will select a treatment plan that is right for you based on the size of your rash, where it is on your body, your age, your overall health, and other things. Common treatments include:
Light therapy-A doctor shines ultraviolet light on your skin to slow the growth of skin cells. PUVA is a treatment that combines a medicine called psoralen with a special form of ultraviolet light.
Methotrexate-This drug can cause bone marrow and liver disease as well as lung problems, so it is only for serious cases. Doctors closely watch patients. You will have to get lab tests, perhaps a chest X-ray, and possibly a liver biopsy.
Retinoids-These pills, creams, foams, lotions, and gels are a class of drugs related to vitamin A. Retinoids can cause serious side effects, including birth defects, so they are not recommended for women who are pregnant or planning to have children.
Biologic treatments-These work by blocking the body's immune system (which is overactive in psoriasis) to better control the inflammation from psoriasis. Biologic medications include adalimumab (Humira), brodalumab (Siliq), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) etanercept (Enbrel), guselkumab (Tremfya), infliximab (Remicade), ixekizumab (Taltz), secukinumab (Cosentyx), tildrakizumab (Ilumya), and ustekinumab (Stelara).